Page 41 - Market Analysis Report of Optical Communications Field in China & Global market 2025
P. 41
cutoff wavelength on system transmission performance. Table1 Test raw data of λCC on cabled/uncabled fibers
The results from both simulations and experimental studies
demonstrate that G.654.E fibers exhibit no significant SNR Fiber type fiber color uncabled cabled Delta (nm)
degradation in the S-band. Furthermore, the impact of fiber(nm) fiber(nm)
the cutoff wavelength on MPI is negligible. This research G.652.D blue -32
provides critical theoretical support and experimental G.654.E orange 1156 1124 -23
validation for the practical application of G.654.E fibers in Green 1152 1129 -32
S-band transmission. Brown 1157 1125 -33
Gray 1158 1125 -33
2. Discussion on the Methods of Cut-off Average 1160 1127 -30
Wavelength Testing blue 1156 1126 -100
orange 1407 1307 -102
The current ITU-T international standards set specific Green 1407 1305 -102
technical indicator requirements for the cut-off wavelength Brown 1406 1304 -115
of single-mode fibers. For all subcategories of G.654 fibers, Gray 1417 1302 -103
the cable cut-off wavelength should not exceed 1530 nm. Average 1407 1304 -105
According to the stipulations of the GB/T 15973.44-2017 1409 1304
standard for cut-off wavelength testing methods, the tests
should be conducted on either 22m uncabled fiber or 22m for G.652.D fiber is 30nm, while for G.654.E fiber, the
cabled fiber. The arrangement of the fibers needs to strictly difference reaches 100nm. This discrepancy is related to
follow the standard's specifications, as shown in Figures 1 the refractive index profile of the fiber. G.654.E fiber has
and Figures 2 respectively. a larger effective area and a lower core-cladding refractive
index difference, making it more sensitive to bending. As a
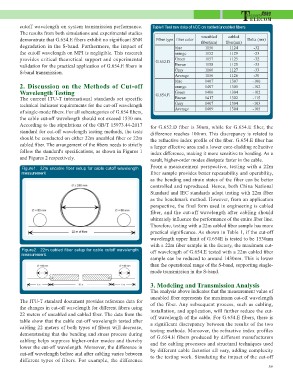
Figure1. 22m uncable fiber setup for cable cutoff wavelength result, higher-order modes dissipate faster in the cable.
measurement From a measurement perspective, testing with a 22m
fiber sample provides better repeatability and operability,
Figure2. 22m cabled fiber setup for cable cutoff wavelength as the bending and strain states of the fiber can be better
measurement. controlled and reproduced. Hence, both China National
Standard and IEC standards adopt testing with 22m fiber
as the benchmark method. However, from an application
perspective, the final form used in engineering is cabled
fiber, and the cut-off wavelength after cabling should
ultimately influence the performance of the entire fiber line.
Therefore, testing with a 22m cabled fiber sample has more
practical significance. As shown in Table 1, if the cut-off
wavelength upper limit of G.654E is tested to be 1530nm
with a 22m fiber sample in the factory, the maximum cut-
off wavelength of G.654.E tested with a 22m cabled fiber
sample can be reduced to around 1430nm. This is lower
than the operational range of the S-band, supporting single-
mode transmission in the S-band.
The ITU-T standard document provides reference data for 3. Modeling and Transmission Analysis
the changes in cut-off wavelength for different fibers using
22 meters of uncabled and cabled fiber. The data from the The analysis above indicates that the measurement value of
table show that the cable cut-off wavelength tested after uncabled fiber represents the maximum cut-off wavelength
cabling 22 meters of both types of fibers will decrease, of the fiber. Any subsequent process, such as cabling,
demonstrating that the bending and stress process during installation, and application, will further reduce the cut-
cabling helps suppress higher-order modes and thereby off wavelength of the cable. For G.654.E fibers, there is
lower the cut-off wavelength. Moreover, the difference in a significant discrepancy between the results of the two
cut-off wavelength before and after cabling varies between testing methods. Moreover, the refractive index profiles
different types of fibers. For example, the difference of G.654.E fibers produced by different manufacturers
and the cabling processes and structural techniques used
by different cable factories all vary, adding complexity
to the testing work. Simulating the impact of the cut-off
39